Step 1 of 5: AI Self-Service Without Compromise – Identifying the Perfect Fit
Step 2>>
Gartner predicts that “customers [soon] will prefer using speech-driven interfaces to other forms of self-service when given a choice.” That shift is being driven by advances in conversational AI, which uses advanced speech recognition and natural language processing to automate more calls, chats, and texts than ever before. Delivery over the cloud has made integration with existing contact center systems easier and more seamless, as well. This combination has led to the growing adoption of AI-powered virtual agents to automate conversations traditionally handled by live agents.
This is the first of a five-part blog series that outlines the Five Best Practices for AI Self-Service Without Compromise.
Use this guide to automate your contact center and Customer Experience (CX) with AI self-service in voice, chat, and text.
Best Practice #1: Identify the Perfect Call Types & Chats for AI-Powered Virtual Agents
For years, you have been collecting data about what happens inside your contact center: agent performance, call volumes, handle times, satisfaction scores, and much more. Any self-service implementation project starts by leveraging this data.
Before introducing AI-powered virtual agents to your contact center, it is critical to ask yourself one question:
“What are the top reasons customers are calling our organization?”
It’s essential to think in terms of call types. Even as contact volumes in chat and SMS text grow, best practice implementations start in voice first, where the ROI is the greatest, then scale the same experience digitally for an omnichannel CX from a unified application.
Automate More with Virtual Agents
Once you have the list of top call types being handled by your live agents, you can begin to evaluate whether or not they are strong candidates for conversational AI automation. Typically, these are the high volume, repetitive calls that come into the contact center that live agents are still handling. Since these call types are process-driven, live agents can almost feel like a robot doing the job. However, they are still too complicated for your touchtone or directed dialog IVR since automating them requires:
- Advanced speech recognition;
- Access to customer data with the ability to read and record that data;
- Dynamic speech to communicate conversationally with customers;
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract intent;
- Cognitive abilities to do something intelligent with what was heard.
This is where conversational AI excels and, ultimately, why it is being adopted at such a rapid rate. What’s more, it allows live agents to be upskilled to do what only humans should do.
Using this logic, it becomes clear that there are dozens of call types that are perfect for virtual agents, as well as some that should remain with human agents. In saying “perfect for automation,” it is not that AI agents will automate 100% of the call volume; instead, consider how many of those calls follow the same, repetitive process over and over with little to no exception. For example, even if only 40% of your order status calls follow this “happy path,” choosing to automate will still equate to substantial cost-savings. For those calls with exclusions that fall outside the “happy path,” virtual agents simply transfer to the live agent along with the data collected to that point, so live agents can simply pick up where the call left off.
Which Call Types Are Perfect for AI Automation
Don’t get caught up in thinking that virtual agent containment rates should be 95% for a given call type to be a candidate for automation. It’s not about trying to contain everything in automation. It’s rather about automating the “happy path” where an AI agent can deliver an experience as good as or better than a live agent. This helps you upskill your live agents to handle the exclusions that only a human should handle. By using business rules extracted from your customer data, it’s easy to create “guardrails” for the virtual agent to stay in its lane and provide an effortless CX without ever frustrating callers.
Here are some examples of common call types that are complex, but still perfect for natural language automation because they are process-driven:
- Order management calls, such as placing orders, order status, and returns
- Reservations & Scheduling calls, such as making reservations, scheduling appointments and outbound confirmations
- Billing & Payment calls, such as make a payment, collections, and payment plans
- Tech Support calls, such as Tier 1 Tech Support and password reset
- Account & Membership calls, such as account authentication and update account information
- See more on our Solutions pages
This is the benefit of cloud-based AI agent solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing telephony and CRM investments. You’re able to automate one call type or chat at a time, starting with the types that are perfect for self-service without sacrificing an ounce of CX. For example, J&B Medical Supply, a healthcare supplies retailer, began by automating outbound calls to remind customers about reordering supplies because that’s where the greatest ROI was; then, the supplier began picking off more than a dozen additional call types – patient authentication, order status, authorizations, account updates, etc. – as part of its ongoing transformation to AI automation.
Simple & Complex Call Types and How to Identify Them
The easiest way to think about call types is as either simple, complex, or human-only.
Simple – Simple inquiries are basic conversations that can be fulfilled with touchtone IVR self-service or simple chatbot. These constitute a large portion of overall volume. However, the limitations of these systems mean that many customers “zero out” or request transfer to a live agent due to a poor CX, lengthy and confusing menus, or lack of natural language voice capabilities to help with other inquiries or questions that do not need human involvement. For this reason, organizations are replacing simple automation with conversational AI self-service.
Complex – Complex calls have traditionally been handled entirely by live agents. To automate them requires conversational AI. With the ability to understand intent from natural language and the ability to read and record data, AI-powered virtual agents are like call center virtual assistants, and can mimic live agent behavior across call types that do not require human judgment or complex, critical thinking. Since even multi-turn conversations typically follow the same consistent process, virtual agents can be architected to follow the “happy path” where the experience is as good or better than a live agent. If intent is ever in question or the customer goes outside the “happy path” (i.e. customer doesn’t know account information), exclusions are simply transferred to live agents with a screen pop of gathered data for the finishing touch.
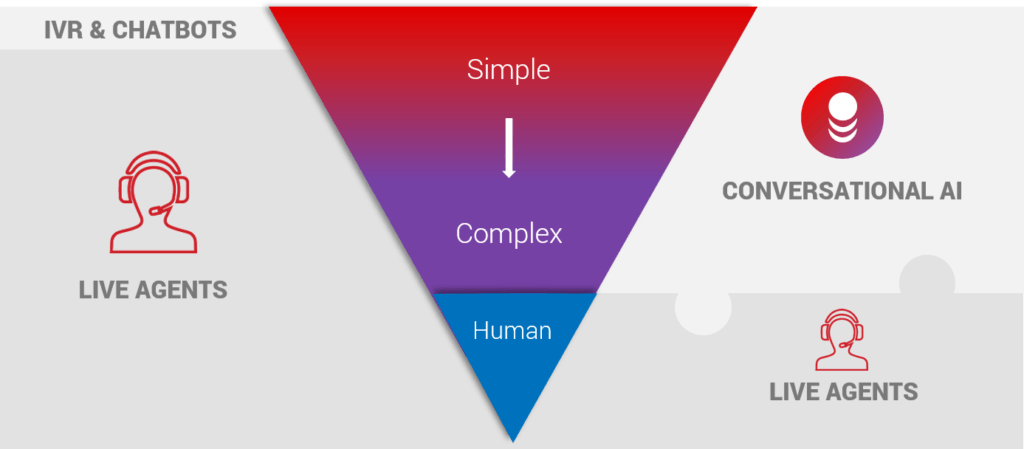
Human Only – This is the best way to describe conversations that must be handled by a human agent. While virtual agents are highly proficient in process-driven calls, humans are still key in providing customer care for non-repetitive, corner cases that require judgment and/or complex critical thinking. By automating simple and complex call types with virtual agents, live agents are upskilled to maximum productivity and focused on doing what a human should do.
For example, simple call types might include order status, payments, or appointment confirmations. Complex call types might include hotel reservations, roadside assistance, tech support, or scheduling an appointment. Human-only call types might include First Notice of Loss and medical assessments. Each industry and business will be a bit different. It ultimately comes down to assigning call types as automation-only, automation + human (humans to handle exclusions), or human-only.
Within these categories, there are typically 2-3 call types that are the most obvious candidates to start your AI self-service journey that will deliver an almost immediate ROI.
Virtual Agents Deliver ROI in the Right Use Cases
One example is for a large global insurer that identified payments as the best place to start with AI self-service because the process could not be automated with their touchtone IVR. After a successful implementation in voice, they scaled the payment solution to SMS text. The insurer is collecting at a higher rate than expected while improving the CX. Now that they have seen how customers interact with the system and the resulting ROI, they have nearly ten call types on their roadmap for customer service automation. By taking a “crawl, walk, run” approach, you’ll achieve the lowest risk implementation possible instead of trying to do everything at once.
This is the first Best Practice in our guide because it is without question the most important part of the journey. By identifying the right call types to automate, you are setting your AI self-service project up for success. Best Practice Two, “Virtual Agents Need Guardrails,” will detail conversation design and proper integration so that the virtual agent solution provides a CX that is as good or better than a live agent every time.